Hardware
Services
Case
Most computer hardware components are housed in cases, which are typically plastic or metal enclosures. A desktop version is typically made in a size that fits under a desk;…
READ MORE
Expansion Cards
In a computer, an expansion card is a complete prefabricated circuit that is attached to the expansion slot on the motherboard and provides additional functionality to the system.
Storage Unit
A computer’s storage or memory refers to the parts of the system that store and store digital data. Computers are capable of storing data and a component is essential to this process.
Removable Media
It is possible to transfer data between different computers using just one flash drive or optical disk. Their usefulness is dependent upon their ability to be supported in different systems…
Peripherals
Input devices permit the user to input data or control an operation. A mouse and keyboard are a common feature of PCs, but touchpads are a staple of laptops…
Fixed media
Computer data is stored on many media. As a relatively affordable and high-capacity storage option, hard disks are available on almost all older systems.
Our
Superb team !
Comming together is the beginning
Keeping together is progress
Working together is success
Take a look
at our products
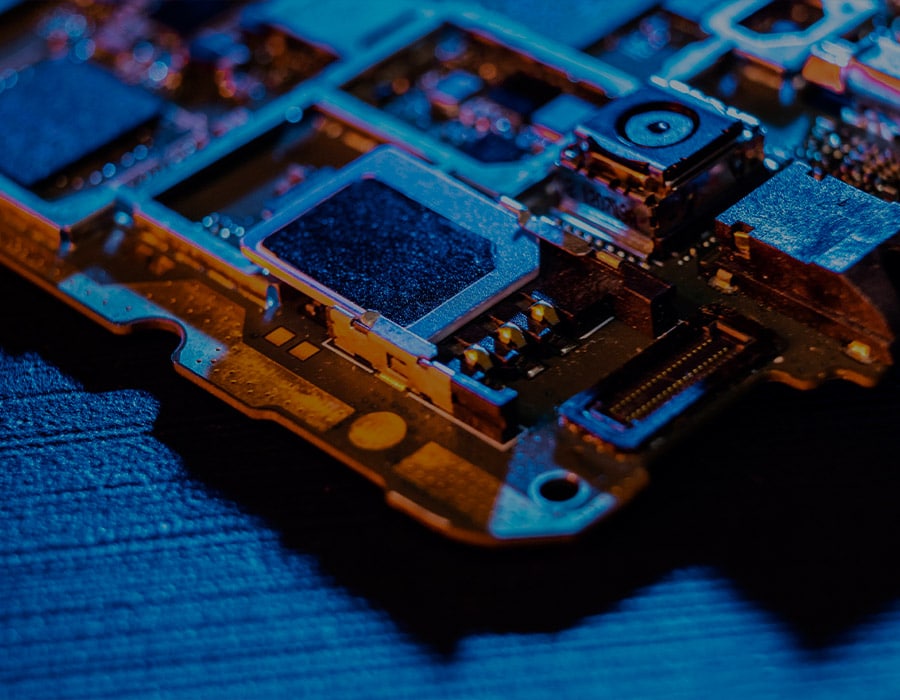
The motherboard
and its components
The motherboard
Motherboards are the main components of a computer. With its many integrated circuits, the mainboard is a large rectangular piece in the heart of a computer.
It connects all other computer hardware such as CPU, RAM, disk drives (hard disk, optical disk, etc.) and other connectable components.
Chipset
The chipset on which the Northbridge circuit is located is responsible for connecting the CPU to other components of the system, such as RAM or main memory.
Random access memory (RAM)
Random access memory or RAM stores data and codes used by the CPU.

Read-only memory (ROM)
ROM stores read-only memory or ROM BIOS. The BIOS is a program that runs when a computer starts up…
, and the process is also called “booting”.The BIOS includes bootloader hardware and power management software. New motherboards have UEFI instead of BIOS.
CMOS Battery
CMOS Battery also connects to the motherboard. This battery provides the power needed to keep time and date in the BIOS.
Central Processor Unit (CPU)
The CPU is responsible for the performance of the computer and performs most of the computing.
This processor is also known as the computer brain and is cooled by a cooling fan. Most new CPUs also have a GPU on their circuit board.
Hardware
Our Services
When using computer hardware, an upgrade means adding new hardware to a computer that improves its performance, adds capacity or new features. For example, a user could perform a hardware upgrade to replace the hard drive with a SSD to get a boost in performance or increase the amount of files that may be stored. Also, the user could increase the RAM so the computer may run more smoothly. The user could add a USB 3.0 expansion card in order to fully use USB 3.0 devices, or could upgrade the GPU for extra rendering power. Performing such hardware upgrades may be necessary for older computers to meet a programs’ system requirements.
Most modern operating systems employ a method of extending RAM capacity, known as “virtual memory”. A portion of the computer’s hard drive is set aside for a paging file or a scratch partition, and the combination of physical RAM and the paging file form the system’s total memory. (For example, if a computer has 2 GB of RAM and a 1 GB page file, the operating system has 3 GB total memory available to it.) When the system runs low on physical memory, it can “swap” portions of RAM to the paging file to make room for new data, as well as to read previously swapped information back into RAM. Excessive use of this mechanism results in thrashing and generally hampers overall system performance, mainly because hard drives are far slower than RAM.
Software can “partition” a portion of a computer’s RAM, allowing it to act as a much faster hard drive that is called a RAM disk. A RAM disk loses the stored data when the computer is shut down, unless memory is arranged to have a standby battery source. .
Sometimes, the contents of a relatively slow ROM chip are copied to read/write memory to allow for shorter access times. The ROM chip is then disabled while the initialized memory locations are switched in on the same block of addresses (often write-protected). This process, sometimes called shadowing, is fairly common in both computers and embedded systems.
Perform Calculations
There are certain types of computers that are very large and require entire rooms of space. The cost of these computers is hundreds of times greater than that of personal computers. A lot of calculations are performed by these computers, which are often used by governments and large corporations.
Department Systems
Companies started using special-purpose computers in the 1960s and 1970s, including process control systems and laboratory automation systems. These were called minicomputers or small computers.
Fastest Computations
Despite looking like large mainframes, supercomputers are built to handle high computation demands. There is no one technology that qualifies as a supercomputer; rather, it refers to the fastest computers at the time.
